 鲜花( 1181)  鸡蛋( 48)
|
http://blogs.wsj.com/economics/2 ... pensive-u-s-cities/
2 G' x. S+ T/ {. G" Z1 `( z
; O5 p/ Y4 \% Z0 f. w' }Why the Great Divide Is Growing Between Affordable and Expensive U.S. Cities/ u1 d: U4 `5 T$ r
4 A3 F" s1 u1 W. L- U3 Z

! Y) q! z& `4 w. e
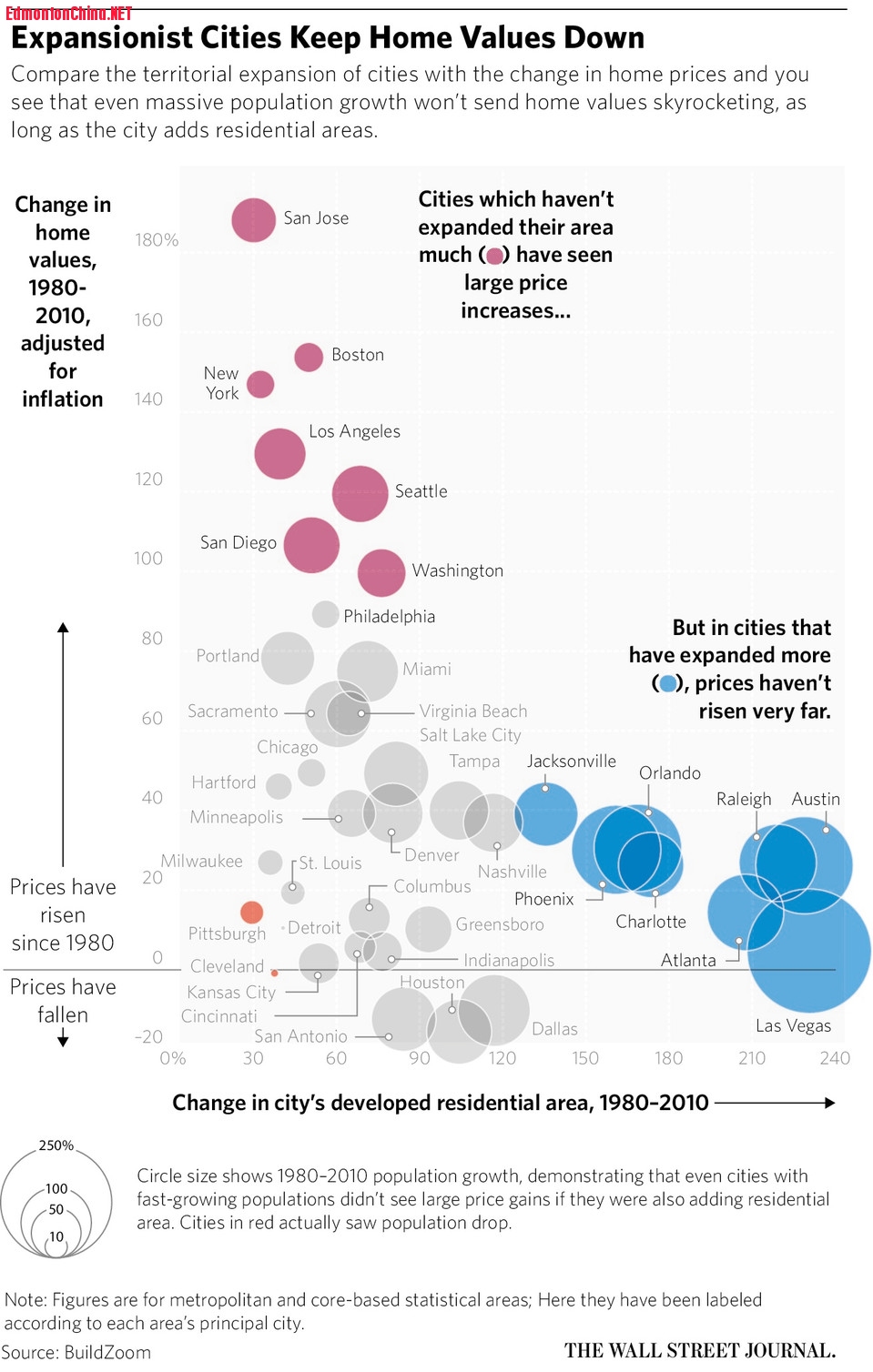
/ l1 y: ~( \ F" ZIn the San Francisco-San Jose area, developed residential land grew by just 30% from from 1980 to 2010, while homes values grew by 188%. PHOTO: MARCIO JOSE SANCHEZ/ASSOCIATED PRESS; j8 M9 `# Q7 c
9 T9 h; m( P0 s8 L4 U7 f& T/ VBy LAURA KUSISTO9 F6 X! u2 J) [3 {
Apr 18, 2016 7:41 am ET8 n* T( F! e; D0 H8 \
46 COMMENTS# D# r8 A1 Z5 g. y+ a0 P6 ?
Across the country, a divide is emerging between cities that are growing outward and remaining affordable and ones that are hemmed in by geography and onerous zoning codes and are becoming more and more expensive.
( J, E+ V) m7 q% R# Y. K( f! K
( E- f$ [/ Z8 L: q4 P$ J( kAs a whole, U.S. cities are expanding as rapidly as they have throughout the last half-century. From the 1950s until the 2000s they have added about 10,000 square miles per decade, or an area roughly the size of Massachusetts, according to research by Issi Romem, chief economist at real-estate site BuildZoom, to be released Monday. But beneath the surface a divide is deepening.
, b/ u) ^% D1 S. o8 }4 Y7 U. _. g m* v, r( t8 i
On the one side are cities such as San Francisco, Boston, New York and Miami that have slowed their pace of expansion dramatically since the 1970s, in part as they have added layer upon layer of building regulations. On the other side are cities concentrated in the southeast and Texas, which have grown outward and seen much slower price growth.) \ x8 m, f% X8 a* r$ J
8 y2 F# |, `) ?
0 C7 H8 v5 L6 O! k
2 m4 V1 O, A7 R NThe developed residential area in Atlanta, for example, grew by 208% from 1980 to 2010 and real home values grew by 14%. In contrast, in the San Francisco-San Jose area, developed residential land grew by just 30%, while homes values grew by 188%.
1 n# Z' h9 t: s8 q0 Q O' ? Z6 g8 t/ Z3 d9 c2 o
The developed residential area in Raleigh, N.C., grew by 219% in the same period, while home values grew by 27%. In Seattle, the developed area grew by 69%, while home values grew by 119%.. A0 {0 S1 x0 a! v7 P
* l6 b5 C+ m' ^, W" O7 H) F
Mr. Romem draws the distinction succinctly: expansive cities versus expensive cities.$ E7 E' }2 N0 ?3 W5 K+ N
7 R) }/ O ^: z+ x+ {( V“If you don’t let the city grow, you’re going to get prices going upward…and see the middle class being pushed out,” Mr. Romem said.
3 W% K7 h6 @! p! ~ G r t2 W( \7 o8 y
& |; b+ a/ i7 g' L8 n0 VMr. Romem’s research reads on its face like an argument for suburban sprawl, which has come under fire both for its environmental consequences and tendency to lead to oversupply that can lead home prices to crash.0 _& b$ @: y o: T& h; N6 S
# I) u h8 D. Y) P: q0 z l
Mr. Romem said ideally cities would relax regulations and build upward rather than outward. But, he said, promoting development on empty fields is more politically feasible than building apartment towers in single-family neighborhoods, and thus likely to ease affordability pressures more quickly.
% V# j0 T4 }2 k5 f5 h9 q5 Q4 |# C0 j; S3 A4 i7 c' O
Many of the more expensive cities are prevented from growing outward by natural barriers, such as oceans or mountains. Those cities are unlikely to grow significantly upward or outward in the next couple of decades, he said, and thus the price divide is likely to continue to widen.
% R' ?6 u9 z/ f! I6 w; ^2 Z" `% s- N# X8 M9 b& A1 O
That could be good news for cities such as Atlanta and Raleigh, N.C., that have long been overshadowed by more economically powerful legacy cities.2 {% e/ X2 F; _9 n& G7 C
/ b- R9 `, p) K3 v5 I( l/ w
“These cities are growing more important because of having more population. They have become more viable places for certain types of firms to locate,” he said. |
|






